Your cart is currently empty!
How Track Sockets Comply with US/UK Voltage Standards
Beginner's Guide to Track Sockets discussion of various topics Outlets Guide remodeling plans
How Track Sockets Comply with US/UK Voltage Standards
Beginner's Guide to Track Sockets discussion of various topics Outlets Guide remodeling plans
Track socket, as an innovative power solution, consists of a powerful power track and three flexible and removable electrical outlets. The design of this set greatly solves the problems of traditional sockets being fixed, inconvenient to use and potential safety hazards. Compared with traditional sockets, the track socket is ideal for modern family life due to its excellent mobility and convenience. It is not only suitable for daily household scenes such as kitchen, bedroom and living room, but also shows incomparable advantages in commercial occasions such as factories and hotels, which require a large number of power access.
The appearance of Track socket marks a revolution in the way we use electricity, and it leads us to a new era of more convenient, comfortable and safe electricity use. Its unique modular design allows users to adjust and expand the power interface according to their own needs, which greatly improves space utilization and power efficiency. In addition, track socket guarantees the safety of electricity consumption and at the same time enhances the neatness and beauty of the indoor environment, bringing an unprecedented convenient experience to our life. It can be said that track socket is not only a power transmission tool, but also a lifestyle upgrade, which makes our life more convenient, comfortable and beautiful.
What countries use the US Standard for track sockets?
First of all, let’s be clear that the U.S. standard sockets are divided into TYPE A and TYPE B, as shown in the following figure:
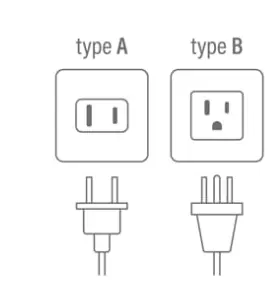
- Use Type A type sockets for Canada, USA, Japan and Mexico
- Use Type B sockets for Canada, USA and Mexico
If you are from the United States, this is a plug that will immediately look familiar to you. It has two flat prongs, and frequently a third prong that is meant to be used as the “ground.” If the cord does not have a ground plug, the wire should still work; however, not every Type A power outlet has a prong for the ground (if it has a ground, it is a Type B plug), so you need to keep this in mind. In addition to the United States, this type of power outlet is found throughout all of North and Central America. It is typically used in Japan as well; however, the Japanese prongs might be a bit smaller. This means that Japanese devices should work fine in plugs in the United States, but the reverse is not always true.-source:worldpopulationreview
Next, I’ll explain in detail whether the wowsocket-track socket US Standard complies with the current and voltage standards of the countries that use American Standard sockets, and whether it is suitable for various scenarios in those countries.
Does the Wowsocket-Track socket comply with U.S. voltage and current standards?
Before giving the answer to the question, first we need to understand the difference between voltage, power and current
These three concepts are closely related and are necessary to know how electricity works. Understanding their differences is important in order not to confuse them as synonyms.
- Voltage:
Voltage allows the transfer of energy from a negative to a positive point. It is measured in volts (V) and determines the strength with which electric current flows. For example, when plugging a device into an electrical outlet, there are usually two holes. One in charge of the positive charge and one in charge of the negative charge; between the two there is a voltage difference which is what makes it possible to get to generate electrical power.
- Power:
In simple terms, electrical power is defined as the amount of energy that a device consumes or generates in a specific interval of time. It is expressed in watts (W) and is calculated by multiplying the voltage by the current. This measurement allows us to understand how much energy is being used or produced by an electrical device at any given time.
- Current:
Current intensity is the magnitude that determines the rate at which a certain amount of electrical charge will flow through a circuit. Current is measured in amperes (A) and its value is obtained by dividing the voltage by the resistance of the circuit.
—source:grupoindustronic
The United States has some of the most complex voltage levels for both residential and commercial applications compared to EU and IEC countries. Basic household voltage in the US is 120V/240V, whereas most IEC countries, including the UK, EU, AUS, and NZ, use a simple 230V single phase and 400-415V three-phase voltage for domestic and small-scale commercial applications.
In addition to 120V single phase voltage, larger electrical systems such as industrial equipment and large commercial buildings may require higher voltages, typically 208, 240, 247, 377, 480, 600 volts, or even more.
- 120V
The standard voltage in the US is 120 volts – 60 Hz single phase supply. This voltage is used for most household and commercial electrical systems, including outlets, appliances, and lighting. The configuration used for the power distribution is known split phase, Edison system or center-tapped where the secondary of the transformer is split in center to provide two level of voltages i.e. 120V and 240V AC.
- 208V
208 volts is a voltage commonly used in the US for commercial and industrial applications. It’s typically used for three-phase power systems, which are used to power larger equipment and machinery.
208-volt circuits are designed to handle the increased electrical load required by these systems, and they are often found in commercial and industrial buildings, such as factories, warehouses, and office buildings.
- 277V
277 volts is a high voltage commonly used in the US for commercial and industrial applications. This voltage is typically used for lighting (e.g. troffers) and other electrical systems that require a higher voltage than the standard 120 volts used in residential applications.
- 240V
In the US, 240 volts is a higher voltage than the standard household voltage of 120 volts. It’s typically used for larger appliances, such as electric ovens, dryers, water heaters and air conditioners, as well as for industrial equipment and large commercial buildings.
- 480V
480 volts is a high voltage commonly used in the US for commercial and industrial applications. This voltage is typically used to power large equipment, such as motors, pumps, and compressors, as well as for lighting and other electrical systems that require a higher voltage than the standard 120 volts used in residential applications.
- 347 & 600
Not common in the US
—source:electricaltechnology
In the United States and Canada, the electrical power supplied to most homes is a split-phase system. That power enters your home at about 240 volts. This 240 volts is split at the main circuit breaker panel into two 120 volt halves, called phases. The 120 volt level is commonly referred to as 110, 115, 120, or 125 volts and is used for lighting and ordinary outlets. Similarly, 220, 230, 240, and 250 volts are used to describe the higher 240 volt level. This higher voltage range supplies larger appliances such as clothes dryers, large air conditioners, and electric vehicle charging.–source:quick220
After understanding the basic voltage and electrical system in the U.S., here are the voltages and currents of the wowsocket-track socket American Standard and the maximum power that can be carried.
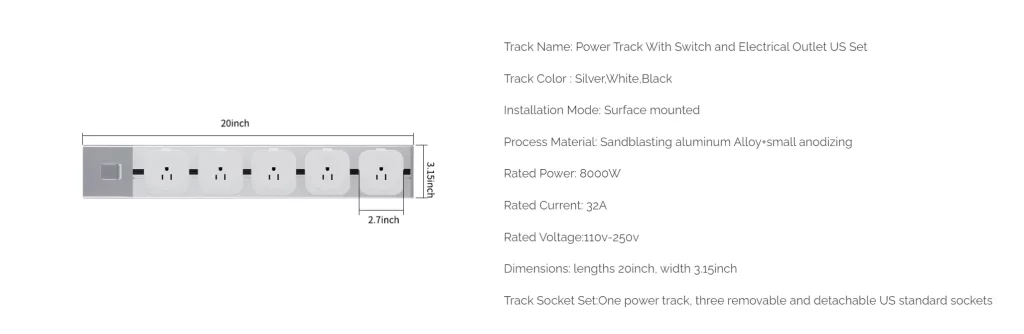
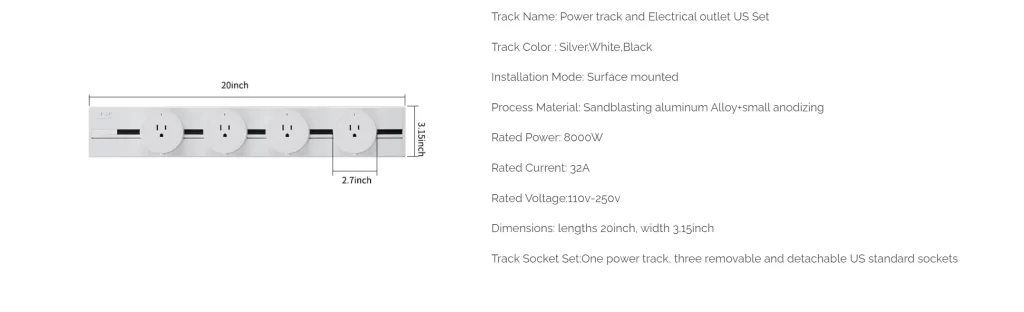
From the above track socket details, we can see that wowsocket-track socket American Standard is fully applicable to the U.S. voltage, and whether it is for residential, commercial buildings or to provide power for industrial equipment is completely acceptable.

Does the Track socket meet Canadian voltage and current standards?
In Canada, the standard voltage is 120 volts (V) with a frequency of 60 Hertz (Hz). This standard applies to all household appliances and electronic devices, and it is the same as in the United States. Therefore, devices from the U.S. can typically be used in Canada without additional voltage conversion.
—source:hkcoupleincanada
Attention:In Canada and Quebec, and in fact everywhere in North America, the standard voltage is 120 V (with a standard frequency of 60 Hz) rather than the 220 volts used in Europe. However, don’t be suprised if you hear or read 110 V. It is an old designation and it is still used by the general public.
—source:authentikcanada
In summary, since the voltage in Canada and the U.S. is the same, wowsocket-track sockets are also suitable for residential and commercial installations in Canada, as well as for factory equipment.
Does the Track socket comply with Japanese voltage and current standards?
Electric sockets in Japan have a voltage of 100V, which is actually quite unique in comparison with most other countries. The United States and Canada have a similar voltage at 120V, but most of Europe, Australia, and New Zealand have voltages around 230V – 240V.
The following are Japanese standards for electrical equipment
- Voltage: 100V
- Frequency: 50Hz – 60Hz
- Electrical Plug Type: Type A
—source:japanlivingguide
Attention:
Japan’s electricity runs on different voltage and frequency compared to other countries.
Although 200V has been implemented for some appliances, basically the voltage in Japan is 100V.Appliances brought from overseas might not be used at the voltage in Japan. Note that the plug sockets for 100V and 200V are different in shapes.
The electric frequency is different on either side of the Fujigawa River in Shizuoka Prefecture and Itoigawa City in Niigata Prefecture, with 50Hz in the east and 60Hz in the west. The frequency in Kansai Electric’s service area is 60Hz.
And some devices can’t be used at different frequencies
—source:kepco
Some North American equipment will work fine in Japan without an adapter and vice versa; however, certain equipment, especially equipment involving heating (e.g. hair dryers), may not work properly or even get damaged.
The frequency of electric current is 50 Hertz in eastern Japan (including Tokyo, Yokohama, Tohoku, Hokkaido) and 60 Hertz in western Japan (including Nagoya, Osaka, Kyoto, Hiroshima, Shikoku, Kyushu)
—source:japan-guide
In summary, the wowsocket-power track set American Standard can be used in a family home, but as mentioned above, damage to the power track socket can occur when heating equipment is involved.
If you have any insights, discuss them in the comments section!
Does the Track socket comply with Mexican voltage and current standards?
In Mexico, the standard light voltage for most homes and businesses is 127 volts (V) at a frequency of 60 Hertz (Hz). However, it is important to note that there are two types of voltage in the country:
- Single-phase: 120 volts phase-neutral and 240 volts phase-phase.
- Three-phase: 127 volts phase-neutral and 220 volts phase-phase.
Voltage types in Mexico
- Low voltage: it comprises a range that goes from 100 V to 1000 V. Its main function is to supply electric power to homes, industry and public lighting, although voltage levels vary slightly. In the case of public lighting and households, voltages of 110 V and 220 V are used, respectively, while in industry, voltages of 220 V and 440 V can be used.
- Medium voltage: refers to levels higher than 1000 V and reaching up to 34.5 kV. It is generally used to distribute electricity from substations to transformer banks. In Mexico, these facilities operate with a voltage ranging from 1 kV to 25 kV.
- High voltage: it ranges from 34.5 kV to 230 kV. This type of voltage is mainly used to transport electricity over long distances, reaching substations where it is transformed into medium voltage. Due to their high voltage level, these installations require thick cables and high insulators for their proper operation.
—source:grupoindustronic
Lots of talk about why Mexico has 127V.The following is a collection of various discussions:
- The Mexican electrical grid is an unstable grid. It is not well maintained and is subject to highs and low of a frequent nature. 127 volts allows for the electrical distributor (CFE) to have greater flexibility in the power delivery. The 127 standard is slightly higher than the 120 standard for the bulk of the rest of North America but allows for variance of as much as 10% and still be within the confines of what is acceptable. For example: if the grid was set to 120 volts and an increase or decrease occurred of 10% (generally acceptable margin of error for power delivery on a single phase line) the allowance would only be to 132 volts or the low of 108. With 127 volt the variance is slightly more substantial – with an acceptable high of about 138 volt and a low of about 114. Generally the delivery system has a tendency to deliver over-voltage as opposed to under voltage and this 127 standard allows for a greater over voltage delivery with less concern of being outside acceptable parameters. In other words, it takes less work and energy to maintain a 127 volt grid than it does to maintain a 120 volt grid.
- Mexico provides two phases of a 3-phase system at the residential level that are 120 degrees of phase apart, in contrast to US 180 degree split-phase.So in the US the 120-0-120 L1-N-L2 system provides 120 line to neutral and 240 line to line. In Mexico they get 220 line to line and 127 line to neutral. It’s a 127/220 3-phase system whereas US 3-phase systems are 120/208. The ratio of the higher number to the lower number is root(3)
—source:electronics
To summarize, the wowsocket-power track socket is available for both Mexican family homes and commercial buildings
What countries use track socket in the UK Standard?
First of all, let’s be clear about what a standard UK socket looks like, as shown below:
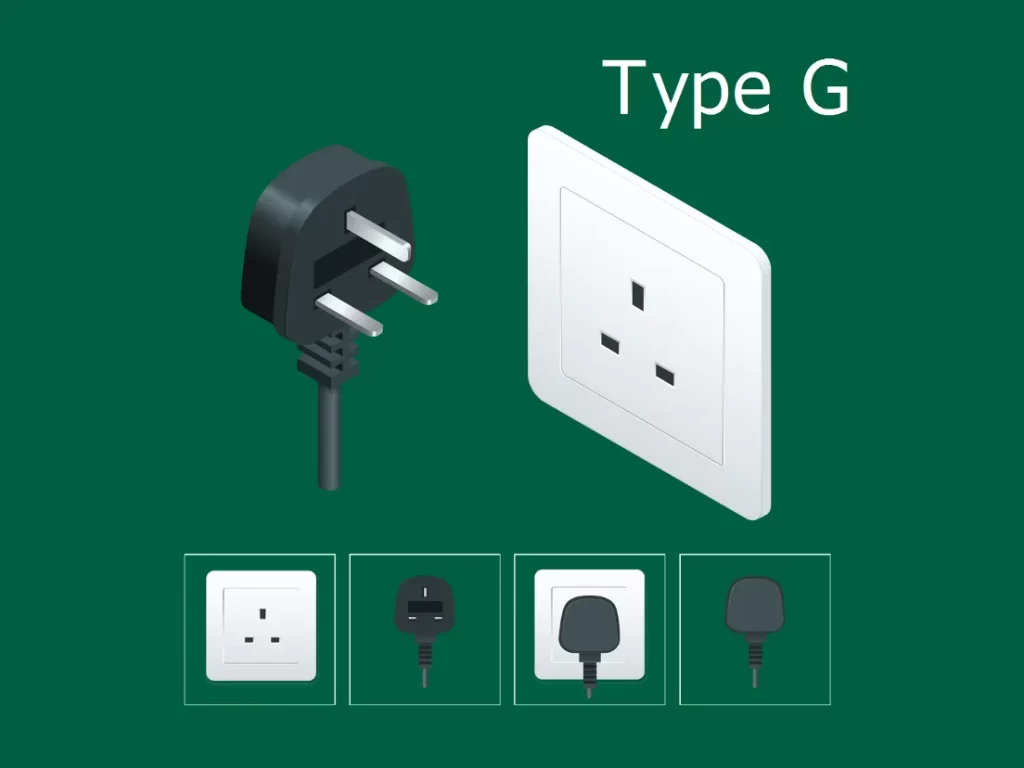

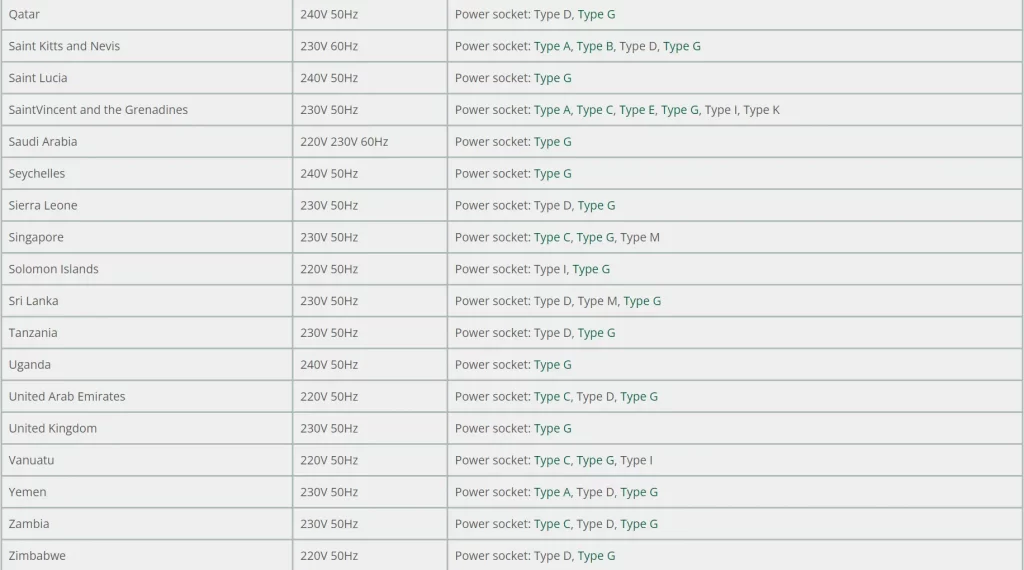
Below is a picture list of some of the countries that use Type G (British Standard) sockets:
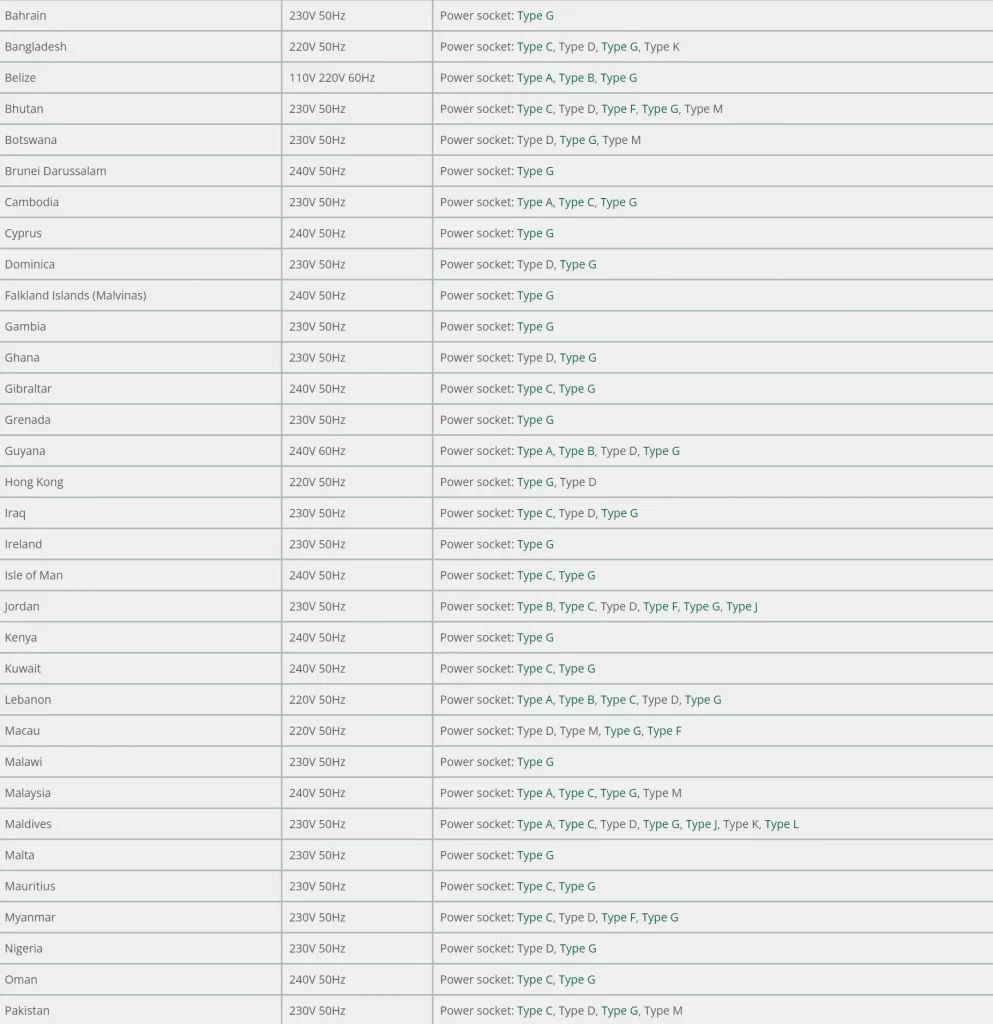
Does the Track socket comply with UK voltage and current standards?
UK AC voltages are classified as low, medium, high and extra high, which are codified as follows:
- Extra high voltage or EHV: 230kV and above
- High voltage or HV: 45 kV to 230 kV
- Medium voltage or MV: 1000 V to 45 kV
- Low voltage or LV: up to 1000V EHV is generated at a high level to account for losses encountered between generation and point of use.
Low Voltage Classification
Low-voltage installations are standard in domestic and commercial premises, and the UK enforces the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) to ensure the safe use of the power supply. This legislation covers most electrical equipment, including domestic appliances, plugs and sockets, power supplies and cables.
Equipment supplied in the LV bracket should be:
- Constructed in accordance with good engineering practice
- Protect against electric shocks through insulation, earthing etc.
- Provide a minimum risk of damage to people, animals or property
- Conform to Schedule 3 safety regulations
A consistent low-voltage supply can lead to power crashes and erratic server operation.
Medium Voltage Classification
Lying in the 1000 V to 45 kV range, an MV installation delivers better reliability and performance with sustainable operations and switchgear. Factories and industrial facilities use medium voltage, where amperage decreases as voltage increases for greater efficiency.
MV networks use power more responsibly and economically, putting them at the heart of safer, more energy-efficient and sustainable installations as we transition to greener ways of using electricity.
Factories that rely on MV or HV supply require their own electrical substation to step down the voltage levels for distribution across a plant. Depending on the size of the facility, several substations may be necessary to provide energy for groups of buildings.
High Voltage Classification
High voltage networks in the UK are operated by National Grid in England and Wales, Scottish Power, Scottish Hydro and Northern Ireland Electricity. These DNOs own and operate the towers and cables that transmit electricity to homes and businesses.
Higher Voltage networks have several advantages:
- Reduced power loss through transmission lines
- The reduced voltage drop across the circuit
- Reduced costs through the use of lightweight cables and towers
- Greater network reach
- Improved efficiency and operational savings
High-voltage networks are the most efficient way to deliver electricity from generating stations to domestic and commercial destinations across the country.
—source:networkpowerconnections
Attention:
The UK energy regulator, Ofgem, allows a tolerance of -6% to +10%, which puts the UK’s permissible voltage range of 216 V to 253 V within official limits.
So, for many years, the supply voltage for single-phase supplies in the UK has been 240 V +/- 6%, with a possible range from 226 V to 254 V. For three-phase supplies, the voltage is 415 V +/- 6%, with a range of 390 V to 440 V. Most of the continent has a voltage rating of 220/380V.
The voltage used throughout Europe (including the UK) has been harmonised since January 2003 at a nominal 230v 50 Hz (formerly 240V in UK, 220V in the rest of Europe) but this does not mean there has been a real change in the supply.
Instead, the new “harmonised voltage limits” in most of Europe (the former 220V nominal countries) are now:
230V -10% +6% (i.e. 207.0 V-243.8 V)
In the UK (former 240V nominal) they are:
230V -6% +10% (i.e. 216.2 V – 253.0 V)
This effectively means there is no real change of supply voltage, only a change in the “label”, with no incentive for electricity supply companies to actually change the supply voltage.
To cope with both sets of limits all modern equipment will therefore be able to accept 230V +/-10% i.e. 207-253V.
—source:leadsdirect
Here are the details of wowsocket-power track socket UK Standard:
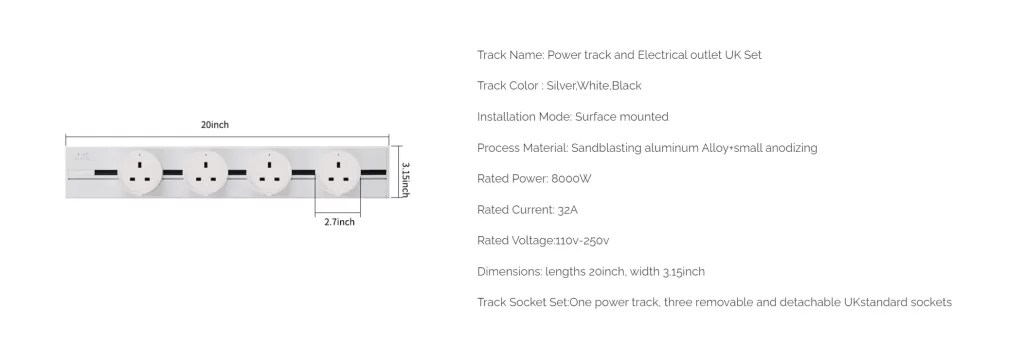
In summary, the wowsocket-power track socket is compliant with the British Electrical Code and is suitable for use in residential and commercial buildings in the UK.
Does the Track socket comply with the voltage and current standards of the United Arab Emirates?
Electricity is supplied in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) at 230 volts AC, 50 Hertz (Hz).
Electric plugs used in the UK, Ireland, Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, and some African and Middle Eastern countries are also of the British Type G model, so electronics and appliances from those countries generally may be used in the UAE without an adapter.
Attention :
If the appliance operates between 220–240 volts, 50 Hz, it may still require a plug adapter, but it will work in the UAE without a voltage converter.
If the appliance operates between 110–120 volts, 60 Hz (as with appliances from most North and South American countries), it may require both an adapter and a voltage converter/transformer. The converter/transformer adjusts the power coming from the 230V outlet down so that the 120V appliance is not overloaded. You can purchase dual-voltage hair dryers and curling irons that work with multiple electric currents.
—source:atozworldtravel

Based on the information in this chart we can learn that the wowsocket-power track socket uk standard is fully compatible with the United Arab Emirates’ electrical system and suitable for scenarios such as residential, but please note that, as mentioned earlier, a plug adapter may still be required when we are using a high power device that operates between 220-240 volts at 50 hertz. However, no voltage converter is required to work in the UAE!
Does the Track socket comply with Singapore’s voltage and current standards?
![]() Voltage – The mains voltage in Singapore is 230 V which is incompatible with most US appliances (US voltage is currently specified as 120 V + /- 5%).
Voltage – The mains voltage in Singapore is 230 V which is incompatible with most US appliances (US voltage is currently specified as 120 V + /- 5%).
![]() Frequency – The frequency is 50 Hz which is slightly lower than in the US (which operates at 60 Hz).
Frequency – The frequency is 50 Hz which is slightly lower than in the US (which operates at 60 Hz).
—source:wowsocket
The standard voltage in Singapore is 220V/240V at 50 Hz. Singapore uses the British BS1363 three-pronged square pin type socket. Any appliance’s or equipment designed for use in the USA will require an appropriate adapter to convert the voltage and pin configuration for a utilization voltage of 110–120V.
For long distance transmission, the voltage can vary from 5kV to 15kV to 38kV and upwards to 100kV, 500kV or higher voltage classes similar to the USA, depending on the load, distance and level of danger of the high voltage in the area in which it is transmitted. For example, voltages above 15kV class are considered unsafe in densely populated residential areas.
—source:quora
Attention :
If the frequency is different, the normal operation of an electrical appliance may also be affected. For example, a 50Hz clock may run faster on a 60Hz electricity supply. —source:electricalsafetyfirst
But for the wowsocket-power track socket, as long as the rated voltage is not exceeded, the above problem will not occur, because the standard voltage of the new Gabo is 230V, which is smaller than the maximum voltage that the track socket can withstand.
FAQS
Are electrical outlets and power tracks the same?
Different, the power track can withstand up to 8000w, while the electrical outlet can withstand up to 2500w.
Can the power track use both UK and US standard sockets?
Of course, sockets of different standards can be used at the same time, but be careful to choose the socket that meets your needs.
- Power Socket Track: Easy Setup and Safe Use Tips
- Track Socket Problems: Troubleshooting Common Issues
- High-Speed Black Electrical Outlet with USB – Ideal for Modern Homes
- How Safe Are Power Strips? Essential Tips for Safe Usage
- Why Backstabbing Electrical Outlets Are Dangerous
2,950 点击次数


发表回复